Masking with Unreal
When developing for Varjo XR headsets, you can mask specific objects to act as a “window” into the real world. This is especially useful if you want to see real-world elements such as instruments or controller devices in the virtual environment.
Varjo Compositor uses the alpha value of a layer to blend between the image from the client application and that from the video pass-through (VST) cameras. If VST rendering is enabled and the layer is not flagged as opaque, every pixel in the color buffer with an alpha value smaller than 1.0 will be blended with the VST image. If the color of the pixel in the color buffer is RGBA(0,0,0,0), only the VST image will be visible.
Follow these simple steps to add a VST mask to your Unreal project.
Creating a mixed reality mask
Enable mixed reality for Varjo OpenXR plugin following the steps in Mixed Reality with Unreal.
Start by adding a Static Mesh Actor to your scene. The mesh will act as a mask for the video pass-through image and can be any shape.
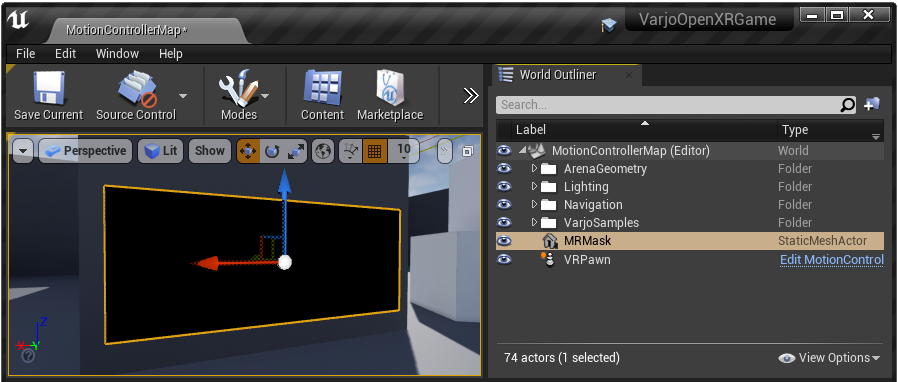
You can utilize the custom depth buffer to create the VST mask. Go to Project Settings > Rendering > Postprocessing and set Custom Depth-Stencil Pass Enabled to enable the custom depth buffer.
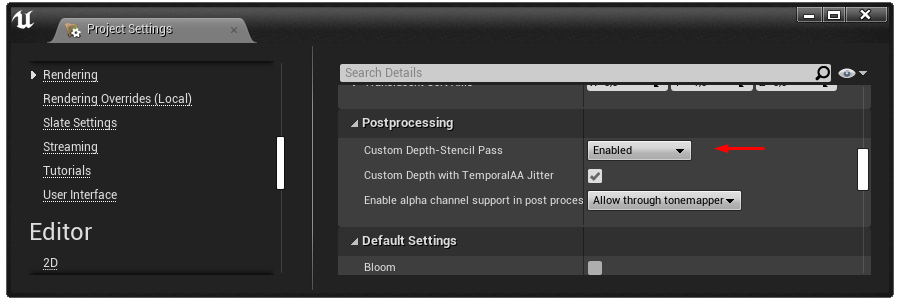
Once you have the custom depth buffer set up, you have to make the mask mesh write into it.
Select the created Static Mesh Actor and enable Render CustomDepth Pass in Details > Rendering.
The mask object is now ready. Follow the steps in Mixed Reality with Unreal to set up custom post processing and open the post process material in the Material Editor
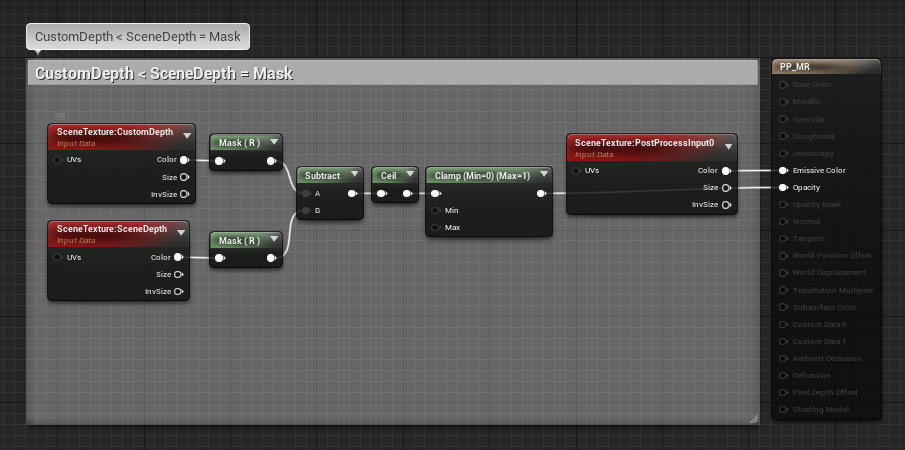
The logic for masking is simple. When CustomDepth is smaller than SceneDepth (= mask object is not behind a non-mask object), output Opacity 0.
Otherwise output Opacity 1.0. If you want to combine masking with mixed reality background, replace 1.0 with the result of the background check.
Click Play and you should see the real world through the mask you created.
You can toggle the mask effect by toggling the Render CustomDepth Pass value in the Static Mesh Actor.