Hand Tracking
Note: you are currently viewing documentation for a beta or an older version of Varjo
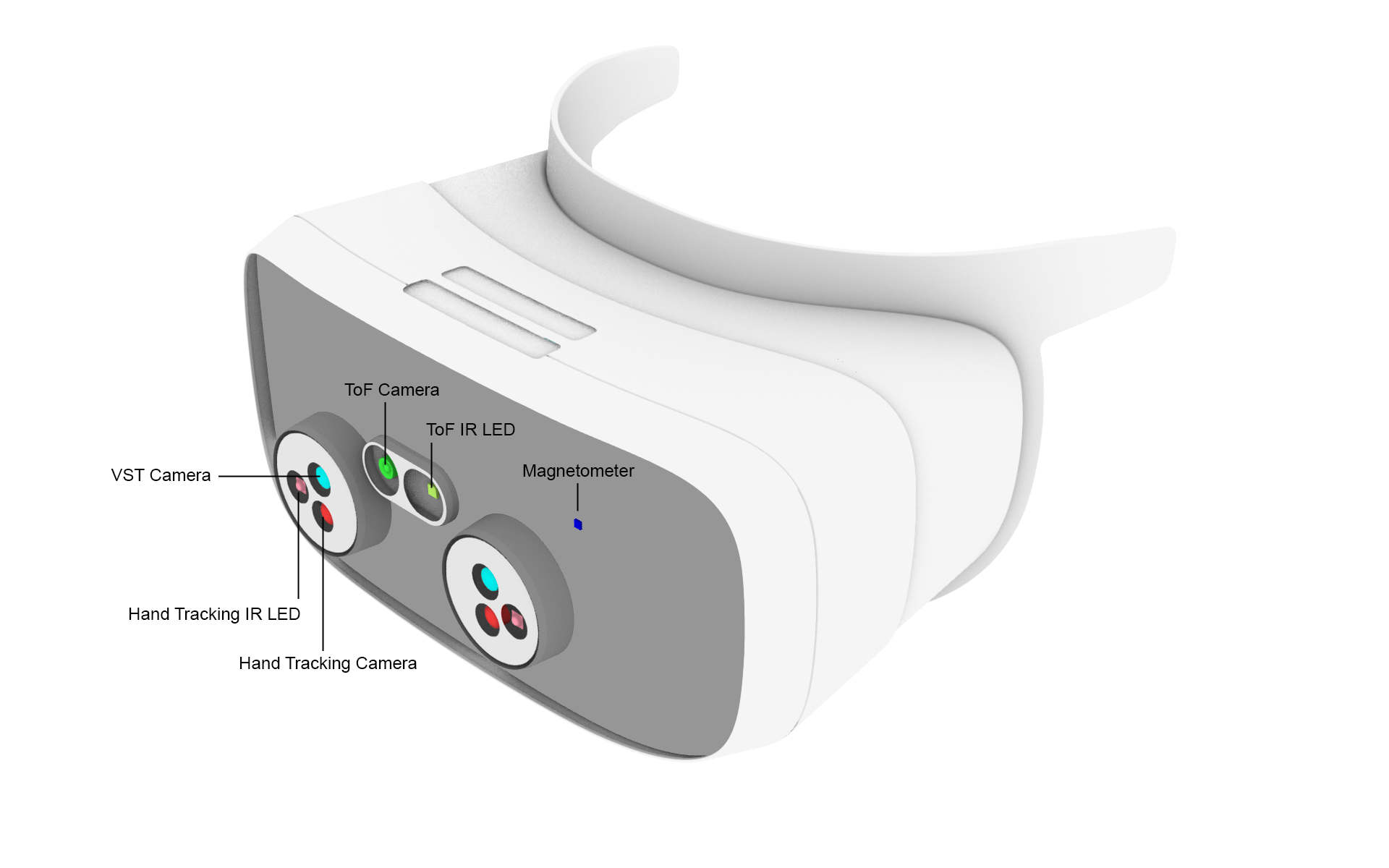
Hand tracking for Varjo is provide by Ultraleap. Varjo XR-4 has an optional hand tracking module. In Varjo XR-3 and VR-3 headsets the hand tracking module is integrated to the headset. Hand tracking lets you reach into the virtual world with your hands and without using a physical controller. Gestures such as pinching, grabbing, and interacting with objects allow for a new level of immersion in your applications.
See the platform-specific documentation for hand tracking:
With XR-3 and VR-3, or with XR-4 with Ultraleap hand tracking module, hand tracking is enabled by default and no additional software is required. If you have previously used standalone Ultraleap sensor, please uninstall its drivers as Varjo Base comes with necessary drivers for the sensors.
XR-3 and VR-3 hand tracking can be disabled in the Headset tab in Varjo Base. With XR-4 you can simply just disconnect the module.
Developing with hand tracking
You can develop hand tracking support for Unreal engine, Unity, or natively. Refer to Ultraleap’s documentation for up-to-date guides on integration and best practices for using hand tracking in XR.
We recommend that you get acquainted with Ultraleap’s XR design guidelines before you start to work on hand tracking interactions. The guidelines provide valuable information for using hand tracking successfully in your project.
Hand tracking offset
When you start to develop with hand tracking for VR-3 or XR-3, make sure to define an offset for the hand position. This is necessary because the head tracking point for your headset differs from the hand tracking point for Ultraleap. XR-4 does not require an offset. Use an offset of 0,0,0 for XR-4.
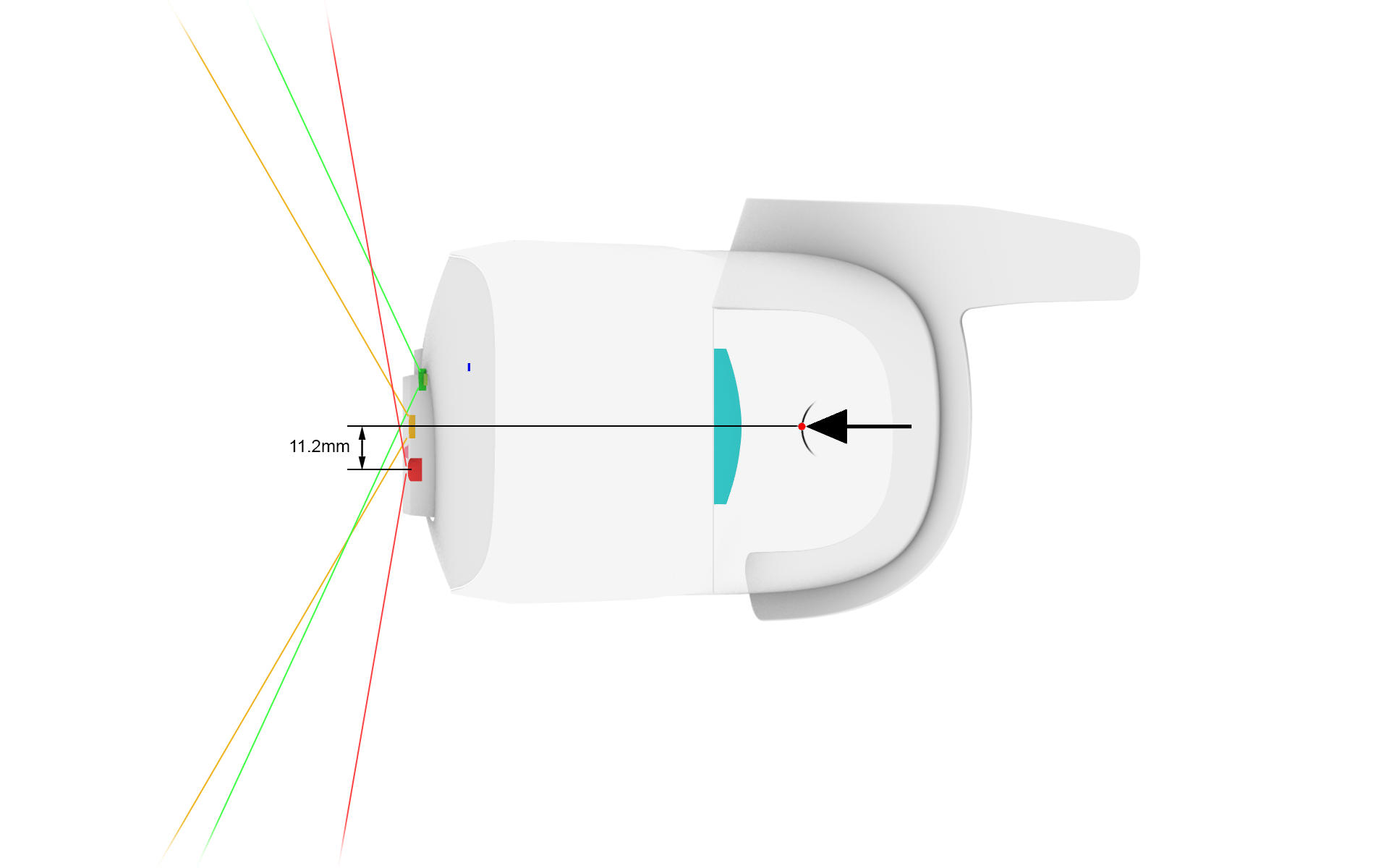
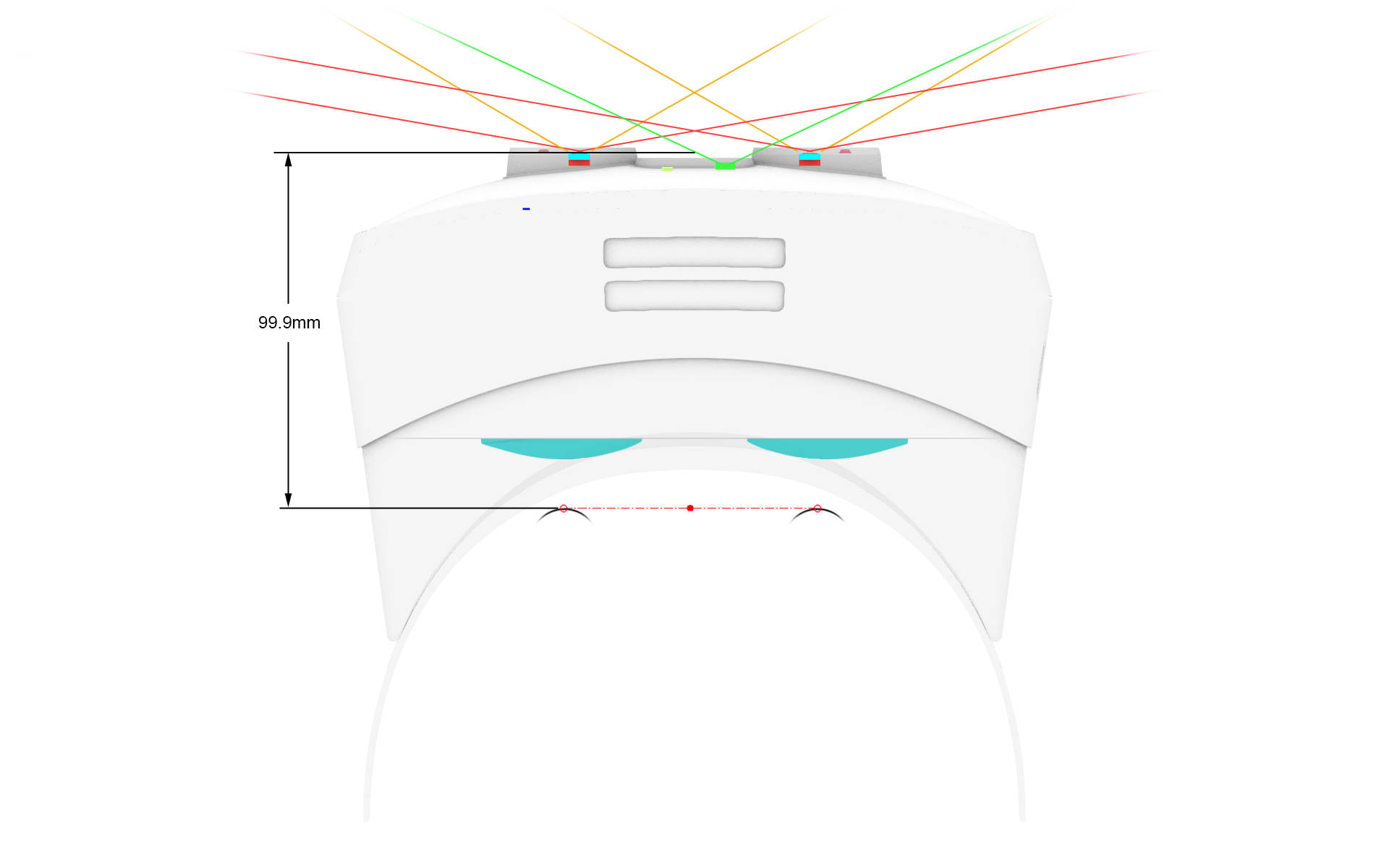
Use the following offset (X = right, Y = up, Z = forward, you may need to use a different scale and coordinate system depending on your engine of choice):
Y: -0.0112 m
Z: 0.0999 m
X tilt: 0°